The global trade landscape has seen a significant transformation in recent years, with emerging markets playing a critical role in this evolution. These nations, which are transitioning from developing to developed economies, are contributing to shifts in trade patterns, economic growth, and industrialization. This blog post delves into the various aspects of how emerging markets are reshaping global trade, discussing their characteristics, role in global supply chains, and their impact on the world economy.
Key Characteristics of Emerging Markets
Emerging markets are characterized by their rapid economic growth, industrialization, and the rise of the middle class. These nations, including countries such as China, India, Brazil, and South Africa, are growing at a pace faster than advanced economies. A key feature driving the growth of emerging markets is their industrialization, where agriculture-based economies are transitioning to manufacturing and services-based economies.
The rise of the middle class in these economies fuels consumer demand, leading to increased domestic consumption and trade activities. As a result, trade growth in emerging markets has surged, with these countries becoming critical players in global trade networks. The potential for high returns on investment makes them attractive destinations for foreign investment, contributing further to their economic growth.
Global Supply Chain Shifts Due to Emerging Markets
Emerging markets are now pivotal in global supply chains. Their low-cost labor, growing infrastructure, and strategic geographic locations have attracted multinational companies to set up manufacturing and production facilities. This integration into the global supply chain has shifted the dynamics of global trade, where goods produced in these markets are exported to developed economies.
The rise of digital technologies and emerging market trends in 2024 also show how these nations are adopting innovations such as automation, artificial intelligence, and advanced manufacturing techniques. These technological advancements are helping emerging markets become more competitive in global trade. Their role in global value chains has not only impacted trade patterns but also led to emerging markets’ global trade impact by driving economic growth across various regions.

Trade Patterns and Geopolitical Influence
The geopolitical landscape has had a profound effect on trade patterns involving emerging markets. Nations such as China, India, and Brazil have established strong trade partnerships with other emerging economies and developed nations alike. The shifts in trade policies, including tariffs, trade agreements, and regional alliances, have further cemented the impact of emerging markets on the economy globally.
For example, China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has expanded trade networks across Asia, Europe, and Africa, increasing China’s influence on global trade. Likewise, India’s trade agreements with Southeast Asian countries and Africa are reshaping the trade corridors in the region. These geopolitical shifts emphasize how emerging markets are influencing trade policies, creating new trade opportunities, and altering traditional global trade dynamics.
Emerging Markets as Commodity Hubs
One of the defining features of emerging markets is their significant role in the global commodity trade. Many of these nations are resource-rich, providing essential commodities such as oil, natural gas, minerals, and agricultural products to the rest of the world. The demand for these commodities in developed economies, particularly in the manufacturing and energy sectors, drives emerging markets’ trade growth.
Countries like Brazil, Russia, and Saudi Arabia, known for their vast natural resources, have become critical players in the global commodity trade. As the world moves towards a more resource-driven economy, emerging markets trade opportunities in commodities are likely to expand further. These economies are key suppliers of raw materials that fuel global industries, making them indispensable to the world economy.

Technological Advancements and Digital Transformation
In recent years, emerging markets have embraced technological advancements, which have propelled their trade growth. Digital transformation, including the rise of e-commerce, fintech solutions, and mobile banking, has revolutionized the way trade is conducted in these economies. As a result, emerging markets’ trade growth has become more agile and efficient, driven by the adoption of innovative technologies.
Technological advancements in countries such as China and India have facilitated seamless trade, improved logistics, and expanded market access. These innovations, particularly in sectors like manufacturing and services, are enabling emerging markets to compete on a global scale. Moreover, digital technologies are helping bridge the infrastructure gaps that have historically hindered the trade potential of emerging markets.

Infrastructure Development: A Catalyst for Trade Growth
One of the main challenges facing emerging markets is their infrastructure deficit. However, many of these nations have made significant strides in improving their infrastructure, particularly in transportation, energy, and communication systems. Infrastructure development is crucial for facilitating emerging markets’ global trade impact, as it improves connectivity, reduces transportation costs, and enhances logistics.
In countries such as India, Indonesia, and Vietnam, government-led infrastructure projects are helping to boost trade by improving access to global markets. Investments in ports, highways, and railways are enabling these nations to become key players in global trade. As infrastructure improves, emerging markets’ trade opportunities are set to grow, providing greater access to international markets.
Trade Barriers and Policy Challenges
Despite their growth potential, emerging markets face several trade barriers and policy challenges. These include protectionist policies, trade restrictions, and complex regulatory environments that make it difficult for foreign businesses to operate. Emerging market trends in 2024 indicate that while these nations are liberalizing trade to some extent, regulatory frameworks can still create significant hurdles.
Trade policies such as tariffs, import restrictions, and stringent customs regulations can limit the trade potential of emerging markets. Additionally, political instability in some regions can create uncertainty, making it challenging for foreign investors to navigate these markets. To fully capitalize on emerging markets’ trade opportunities, these nations need to focus on creating more favorable trade policies that encourage foreign investment and reduce trade barriers.
Sustainability and Environmental Impacts on Trade
Sustainability is becoming an increasingly important factor in global trade, and emerging markets are not exempt from this trend. As the world focuses on reducing carbon emissions and adopting environmentally friendly practices, emerging markets are being pushed to adopt sustainable trade practices. This shift presents both challenges and opportunities for emerging markets’ trade growth.
On the one hand, sustainability initiatives can increase operational costs for companies in emerging markets, as they need to invest in cleaner technologies and environmentally friendly practices. On the other hand, these initiatives can open up new emerging markets and trade opportunities in green industries such as renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and eco-friendly products. The global demand for sustainable goods is growing, and emerging markets have the potential to capitalize on this trend by positioning themselves as leaders in green trade.
Risks and Volatility in Emerging Markets
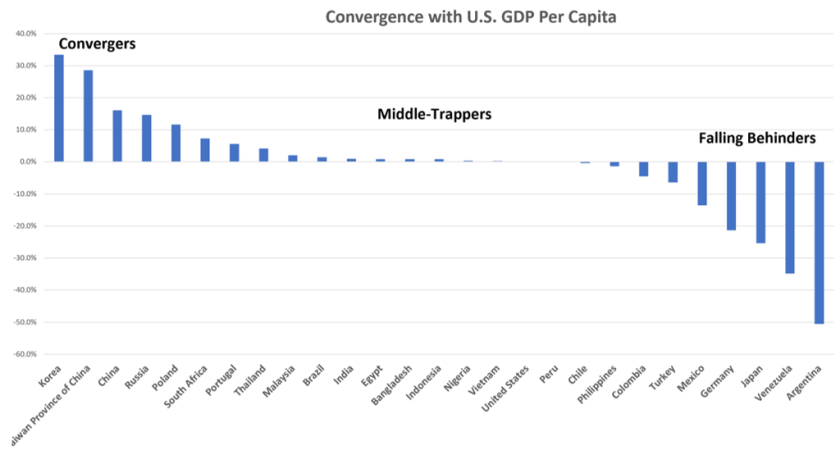
While emerging markets offer significant trade opportunities, they are also prone to risks and volatility. Economic instability, currency fluctuations, inflation, and political risks can all affect trade activities in these nations. For example, the economic crises in Turkey and Argentina in recent years have led to significant disruptions in trade and investment flows.
Emerging markets are often more susceptible to external shocks, such as changes in commodity prices or shifts in global financial markets. Currency devaluation and inflation can also erode the purchasing power of these economies, making it difficult to maintain stable trade relations. Understanding and managing these risks is essential for companies and investors looking to engage in emerging markets trade opportunities.
Impact of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) on Emerging Economies
Foreign direct investment (FDI) plays a crucial role in the growth and development of emerging markets. As these economies continue to integrate into the global economy, they attract substantial FDI from developed nations and multinational corporations. Emerging markets trade opportunities are closely linked to FDI, as foreign investments help build infrastructure, create jobs, and drive economic growth.
FDI also brings with it advanced technologies and expertise that help improve the competitiveness of emerging markets in global trade. Countries such as China, India, and Mexico have benefited immensely from FDI in sectors such as manufacturing, technology, and services. The influx of foreign capital has not only boosted their economic growth but also enhanced their role in global trade.
Future Prospects: Emerging Markets’ Role in Shaping the Future of Global Trade
Looking ahead, emerging markets are poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of global trade. As these economies continue to grow, their share of global GDP is expected to increase, making them even more influential in global trade dynamics. Emerging market trends in 2024 suggest that these nations will continue to drive trade growth, particularly in industries such as technology, manufacturing, and services.
The continued expansion of infrastructure, technological advancements, and trade liberalization will provide new emerging markets with trade opportunities in the years to come. However, these nations will need to address challenges such as political instability, regulatory barriers, and environmental sustainability to fully realize their potential in the global trade landscape.
Conclusion
Emerging markets are no longer just participants in global trade—they are now key drivers of global economic growth. Their impact on global trade is profound, influencing trade patterns, supply chains, and geopolitical dynamics. As these economies continue to evolve, their role in global trade will only become more significant, providing new opportunities and challenges for businesses and investors around the world.





