In today’s rapidly changing economic landscape, businesses are increasingly recognizing the need to embrace zero-waste practices to foster sustainability and reduce environmental impact. The circular economy presents a viable framework for achieving these goals, encouraging companies to rethink their processes, materials, and overall business models. This article delves into how businesses can effectively adopt zero-waste strategies within a circular economy, exploring the principles, benefits, challenges, and successful case studies that exemplify this transformative approach.
Introduction to Circular Economy and Zero Waste
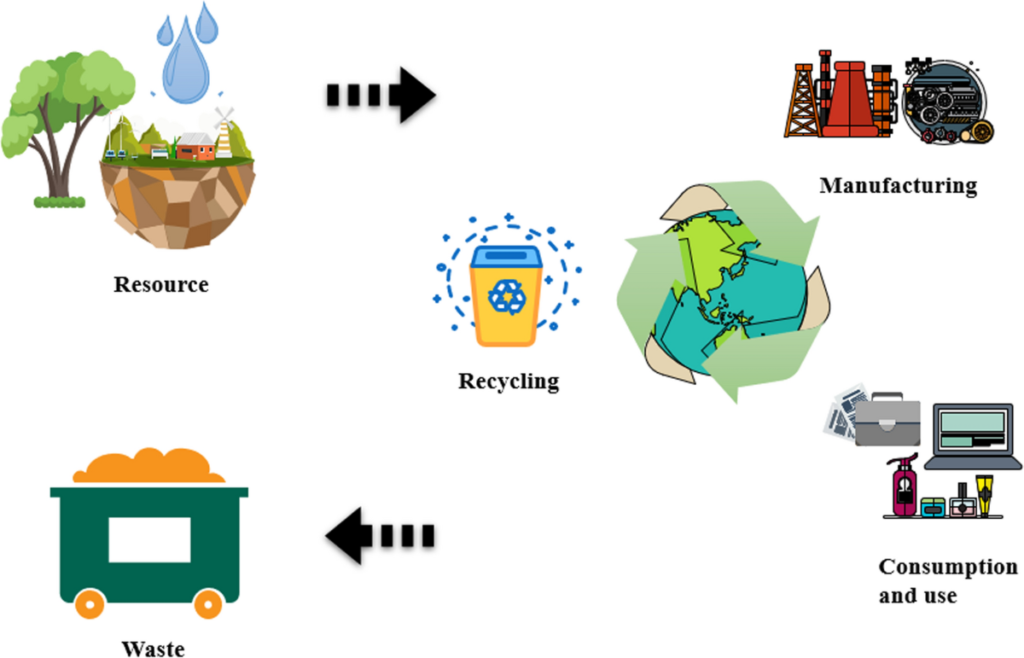
The circular economy is a systemic approach aimed at eliminating waste and promoting the continual use of resources. Unlike the traditional linear economy, which follows a take-make-dispose model, the circular economy focuses on creating a closed-loop system where resources are reused, refurbished, and recycled. In this context, the concept of zero waste plays a crucial role by advocating for the reduction of waste to landfill and encouraging sustainable practices throughout the product lifecycle.
Businesses that embrace zero waste are not only contributing to environmental sustainability but also positioning themselves competitively in a market that increasingly values corporate responsibility. By implementing zero-waste strategies, companies can reduce costs, enhance brand loyalty, and meet the rising consumer demand for sustainable products and practices.
The Shift from Linear to Circular Models
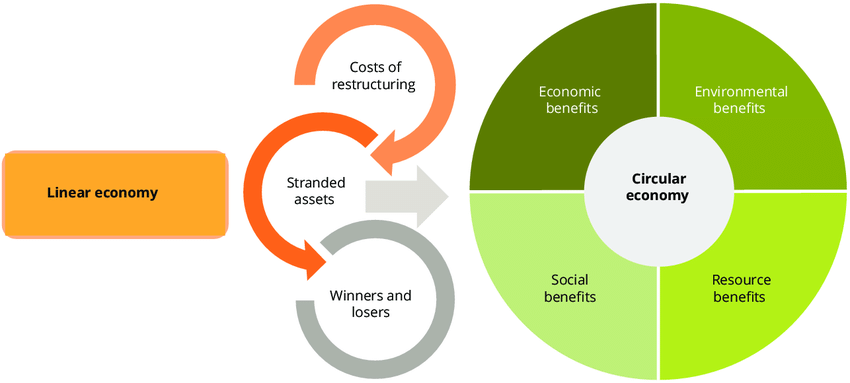
Transitioning from a linear to a requires a fundamental shift in how businesses operate. In a linear model, resources are extracted, used, and discarded, leading to significant waste generation and environmental degradation. The circular model, however, emphasizes the importance of designing products with their end-of-life in mind, allowing materials to be reclaimed and reused.
This shift brings numerous benefits, including reduced resource dependency, lower waste disposal costs, and the potential for new revenue streams through recycling and resale initiatives. Companies that successfully implement circular practices can create a more resilient business model, mitigating risks associated with resource scarcity and regulatory pressures.
Key Principles of Zero Waste in Business

The zero-waste business strategies are founded on a hierarchy of practices that prioritize waste reduction. This hierarchy includes:
- Refuse: Avoiding unnecessary materials and products.
- Reduce: Minimizing waste generation at the source.
- Reuse: Extending the lifecycle of products and materials.
- Recycle: Transforming waste materials into new products.
By integrating these principles into their operations, businesses can significantly reduce their environmental footprint and foster a culture of sustainability within their organizations. For example, companies can initiate programs to train employees on best practices for waste reduction and provide incentives for adopting more sustainable behaviors.
Implementing Circular Practices: Strategies for Businesses
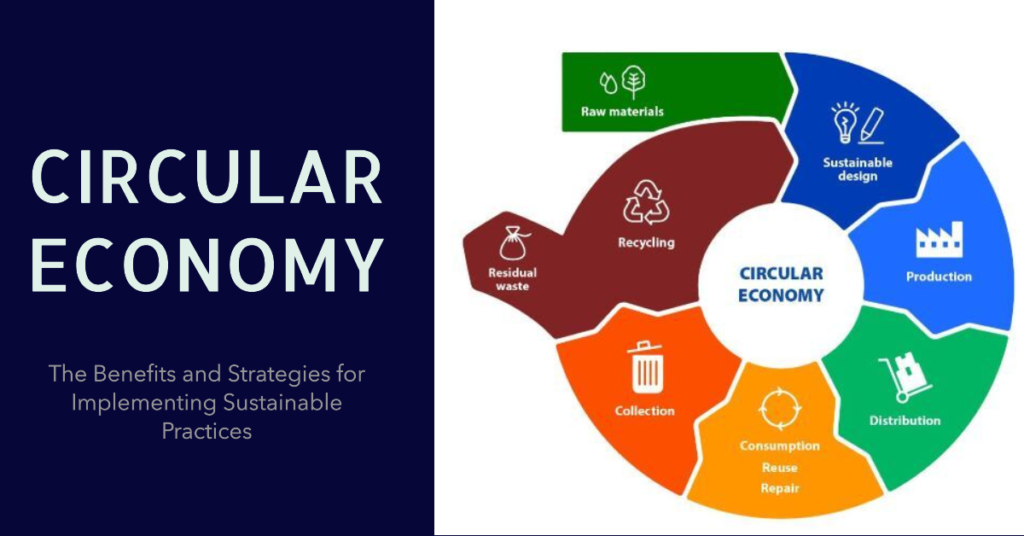
To embrace zero waste, businesses must develop clear strategies for implementing circular practices. This involves:
- Assessing current waste streams: Businesses should conduct thorough audits to identify where waste is generated and explore opportunities for reduction.
- Setting sustainability goals: Establishing specific, measurable targets for waste reduction and resource efficiency helps companies stay focused and accountable.
By taking these steps, companies can lay a strong foundation for integrating circular practices into their daily operations. It also opens up opportunities for innovation, as businesses seek creative solutions to minimize waste and enhance resource efficiency.
Innovative Business Models Supporting Zero Waste

Embracing zero waste often requires businesses to explore innovative models that facilitate resource efficiency. These models can include:
- Product-as-a-Service (PaaS): In this model, companies retain ownership of their products and provide services instead of selling goods outright. This encourages the responsible use and eventual return of products for refurbishment or recycling.
- Take-back schemes: Businesses can establish programs that allow customers to return products at the end of their lifecycle, ensuring materials are recovered and reused.
These innovative approaches not only support zero waste in corporate sectors but also enhance customer loyalty by fostering a sense of shared responsibility for sustainability.
The Role of Technology in Achieving Zero Waste
Technology plays a crucial role in helping businesses embrace zero-waste practices. By leveraging advanced technologies, companies can streamline operations and improve efficiency. Key technological solutions include:
- Data analytics: Businesses can utilize data analytics to track waste generation and identify patterns, enabling targeted interventions for waste reduction.
- Material recovery technologies: Innovations in recycling and material recovery can facilitate the efficient transformation of waste into valuable resources.
The integration of technology into waste management processes not only drives efficiency but also supports businesses in their sustainability objectives.
Collaboration and Partnerships in the Circular Economy
The journey toward zero-waste corporate programs is often enhanced through collaboration and partnerships. Businesses can benefit from:
- Collaborative networks: Joining forces with other companies, NGOs, and government agencies can amplify efforts to promote circular practices and share best practices.
- Industry initiatives: Participating in industry-wide sustainability initiatives can provide valuable resources and support for companies aiming to adopt circular economy principles.
By fostering collaboration, businesses can create a more robust ecosystem that encourages innovation and accelerates the transition to a circular economy.
Challenges and Barriers to Zero Waste Adoption
Despite the numerous benefits, businesses often face challenges when attempting to embrace zero waste. Common barriers include:
- Cultural resistance: Shifting organizational culture to prioritize sustainability can be met with resistance from employees and management alike.
- Resource limitations: Smaller businesses may struggle with the financial and operational resources needed to implement circular practices.
Recognizing these challenges and developing strategies to address them is essential for successful zero-waste adoption. Training programs, stakeholder engagement, and clear communication can help overcome resistance and ensure a smooth transition.
Measuring Success: KPIs for Circular Economy Initiatives
To gauge the effectiveness of zero-waste business strategies, companies should establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that reflect their sustainability objectives. Relevant KPIs may include:
- Waste diversion rates: Tracking the percentage of waste diverted from landfills.
- Resource recovery rates: Measuring the efficiency of material recovery processes.
- Reduction in operational costs: Evaluating cost savings associated with waste reduction and resource efficiency.
Regularly monitoring these KPIs allows businesses to assess progress, identify areas for improvement, and adjust strategies as needed to ensure ongoing success.
Case Studies of Successful Zero Waste Businesses
Examining real-world examples of companies that have successfully implemented zero-waste corporate programs can provide valuable insights. Notable case studies include:
- Patagonia: The outdoor apparel company has adopted a comprehensive sustainability strategy, including product take-back programs and recycling initiatives, exemplifying best practices in the circular economy.
- Unilever: Unilever has made significant strides in reducing waste across its operations, committing to ensuring all of its plastic packaging is recyclable or reusable by 2025.
These examples demonstrate how businesses can effectively integrate zero-waste principles into their operations while achieving significant environmental and financial benefits.
Future Trends in Zero Waste and Circular Economy
As businesses continue to embrace zero waste, several emerging trends are likely to shape the future of circular practices, including:
- Increased regulatory pressure: Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations related to waste management and sustainability, compelling businesses to adapt.
- Consumer demand for transparency: Consumers are increasingly seeking transparency in supply chains, prompting businesses to adopt more sustainable practices.
These trends indicate a growing recognition of the importance of sustainability in business, pushing companies to prioritize zero-waste initiatives as a core part of their strategies.
Conclusion: The Path Forward for Businesses
In conclusion, embracing zero waste within a circular economy framework is not just a trend; it is becoming a necessary business strategy for long-term success. By understanding the principles of the circular economy, adopting innovative business models, leveraging technology, and fostering collaboration, companies can significantly reduce waste and enhance sustainability. The journey may present challenges, but the potential rewards—environmental sustainability, cost savings, and enhanced brand loyalty—are well worth the effort. As the world moves toward a more sustainable future, businesses that commit to zero waste will undoubtedly stand out as leaders in their industries.






2 thoughts on “How Businesses Embrace Zero Waste with Circular Economy”
Comments are closed.