The circular economy represents a transformative shift in how businesses operate, focusing on sustainability and resource efficiency. This model contrasts sharply with the traditional linear economy, which follows a ‘take, make, dispose’ pattern. Instead, the circular economy promotes a restorative approach, emphasizing reuse, recycling, and the sustainable management of resources. This blog post will delve into the various dimensions of the circular economy and its profound impact on business practices, exploring how companies can leverage this model to drive growth and sustainability.
Defining the Circular Economy
At its core, the circular economy is designed to minimize waste and make the most of resources. It envisions a system where products are designed for longevity, repairability, and recyclability. By shifting away from the conventional linear model, which often leads to significant waste generation, the circular economy seeks to create closed-loop systems where materials are continuously reused. This approach not only addresses environmental concerns but also offers a framework for businesses to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
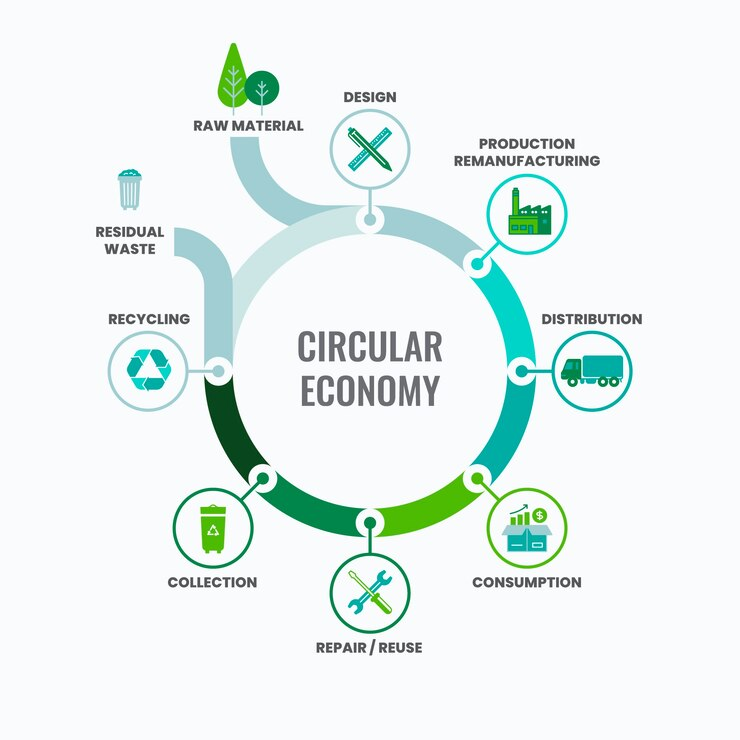
Key Principles of Circular Economy
The principles of the circular economy are foundational to its implementation in business practices. These principles include resource efficiency, waste reduction, and an emphasis on the entire product lifecycle. Businesses adopting a circular economy business model focus on designing products that minimize resource input and maximize durability. This holistic view encourages companies to consider the entire lifecycle of their products, from production to disposal, thereby reducing their environmental footprint and fostering a more sustainable future.
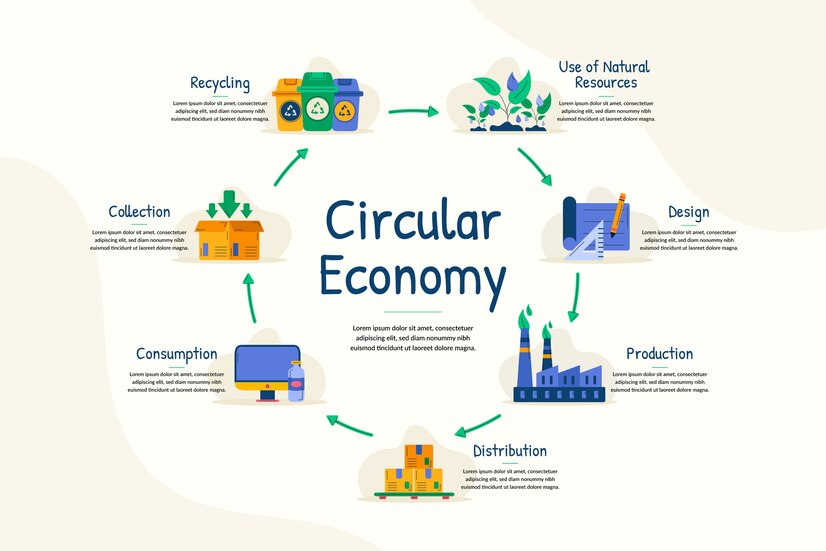
Transformation of Business Models
The rise of the circular economy necessitates a transformation in traditional business models. Companies are increasingly recognizing the value of transitioning from a linear approach to a circular one. For example, businesses are adopting subscription services or product-as-a-service models, allowing customers to use products without owning them outright. This shift not only enhances customer engagement but also promotes more sustainable consumption patterns. Brands such as Patagonia and IKEA have pioneered circular initiatives, showcasing how businesses can effectively implement these models while maintaining profitability.

Environmental Sustainability and Impact
One of the most significant aspects of the circular economy is its potential to drive environmental sustainability. By prioritizing resource reuse and waste reduction, businesses can significantly lower their carbon footprints and contribute to a healthier planet. For instance, the zero-waste movement aligns closely with circular principles, emphasizing the importance of keeping materials in use for as long as possible. Companies that embrace these practices not only fulfill their corporate social responsibilities but also resonate with environmentally conscious consumers, enhancing their brand loyalty and market share.

Economic Advantages of Circular Practices
Adopting circular practices can yield substantial economic benefits for businesses. By optimizing resource use and reducing waste, companies can achieve cost savings and improve their bottom lines. For example, organizations that embrace circular economy trends in 2024 are likely to benefit from reduced raw material costs and improved efficiency in their operations. Additionally, circular practices can open new revenue streams through recycling and upcycling initiatives. This economic rationale reinforces the argument for businesses to shift towards more sustainable models, aligning profit motives with environmental stewardship.

Challenges of Implementing Circular Economy
Despite the numerous benefits, implementing the circular economy presents several challenges. Initial investments in new technologies and processes can be significant, deterring some businesses from making the shift. Furthermore, transitioning to a circular model often requires adjustments in the entire circular economy supply chain. Companies must collaborate with suppliers and customers to establish effective recycling and return systems, which can be logistically complex. Overcoming these barriers necessitates strong leadership, strategic planning, and a commitment to long-term sustainability goals.
Case Studies of Successful Circular Businesses
Examining case studies of successful circular businesses provides valuable insights into best practices and effective strategies. For instance, companies like Unilever and Nike have implemented circular initiatives that demonstrate the viability of sustainable practices. Unilever has committed to ensuring that all of its plastic packaging is recyclable, reusable, or compostable by 2025. Similarly, Nike’s “Move to Zero” campaign aims to reduce waste and carbon emissions while promoting a circular model through its Reuse-A-Shoe program. These examples highlight how businesses can successfully integrate circular principles into their operations while achieving their sustainability goals.
Consumer Demand for Sustainable Products
As awareness of environmental issues grows, consumer demand for sustainable products has surged. The circular economy aligns with this trend, offering businesses an opportunity to cater to eco-conscious consumers. Brands that adopt circular practices often see increased customer loyalty and engagement. By transparently communicating their sustainability efforts, companies can differentiate themselves in a competitive market. The shift towards sustainable consumption reflects a broader societal change, pushing businesses to reevaluate their value propositions and align them with consumer expectations.
Technological Innovations Supporting Circular Economy
Technology plays a pivotal role in facilitating the transition to a circular economy. Innovations in material science, recycling technologies, and digital platforms enable businesses to implement circular practices more effectively. For instance, advancements in tracking and monitoring technologies allow companies to optimize their supply chains and enhance resource management. Moreover, digital platforms that promote sharing and reuse are transforming how consumers engage with products, fostering a culture of sustainability. Embracing these technologies will be essential for businesses aiming to thrive in a circular economy.
Regulatory and Policy Frameworks
Government policies and regulations significantly influence the adoption of circular economy practices. Many countries are implementing frameworks that promote sustainability, such as extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs and regulations aimed at reducing plastic waste. These policies encourage businesses to adopt circular practices and provide a structured approach to resource management. By aligning their strategies with regulatory expectations, companies can enhance their reputations and gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Future Trends in the Circular Economy
Looking ahead, several trends are likely to shape the future of the circular economy. As consumers become increasingly aware of environmental issues, the demand for sustainable products will continue to grow. Companies will need to innovate continually, exploring new ways to implement circular practices while enhancing their value propositions. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and data analytics will enable businesses to optimize their resource management and enhance operational efficiency. The circular economy trends in 2024 will likely focus on collaborative models, encouraging businesses to work together to create systemic change.
Conclusion: Embracing Circularity for Future Success
In conclusion, the rise of the circular economy is reshaping business practices across various sectors, offering opportunities for sustainability, innovation, and economic growth. By understanding and embracing circular principles, businesses can enhance their resilience, respond to consumer demand for sustainable products, and navigate the challenges of the modern market. As we move forward, the commitment to circularity will be crucial for businesses aiming to thrive in an increasingly eco-conscious world. Embracing these practices is not just an option but a necessity for future success.





