The Israel-Lebanon Conflict has resurfaced with renewed intensity, leaving devastating effects on both countries, particularly Lebanon. This recent conflict, primarily between Israel and Hezbollah, is not only a military struggle but also a severe economic crisis for Lebanon, pushing it toward an uncertain future. The ramifications extend beyond human suffering, leading to economic paralysis and long-lasting consequences for critical sectors. Below, we explore in detail the economic consequences of the Israel-Lebanon conflict and how it is impacting the nation.
Introduction to the Israel-Lebanon Conflict
The Israel-Lebanon Conflict has been a central issue in Middle Eastern geopolitics, with tensions often flaring between Israel and Hezbollah, a militant group based in Lebanon. The latest conflict, starting in 2024, has brought devastating consequences, exacerbating Lebanon’s economic crisis. This conflict has pushed the country’s already fragile economy further into the abyss, creating widespread disruptions. The combination of political instability, economic deterioration, and humanitarian crises has created a perfect storm, rendering Lebanon unable to cope with the destruction.
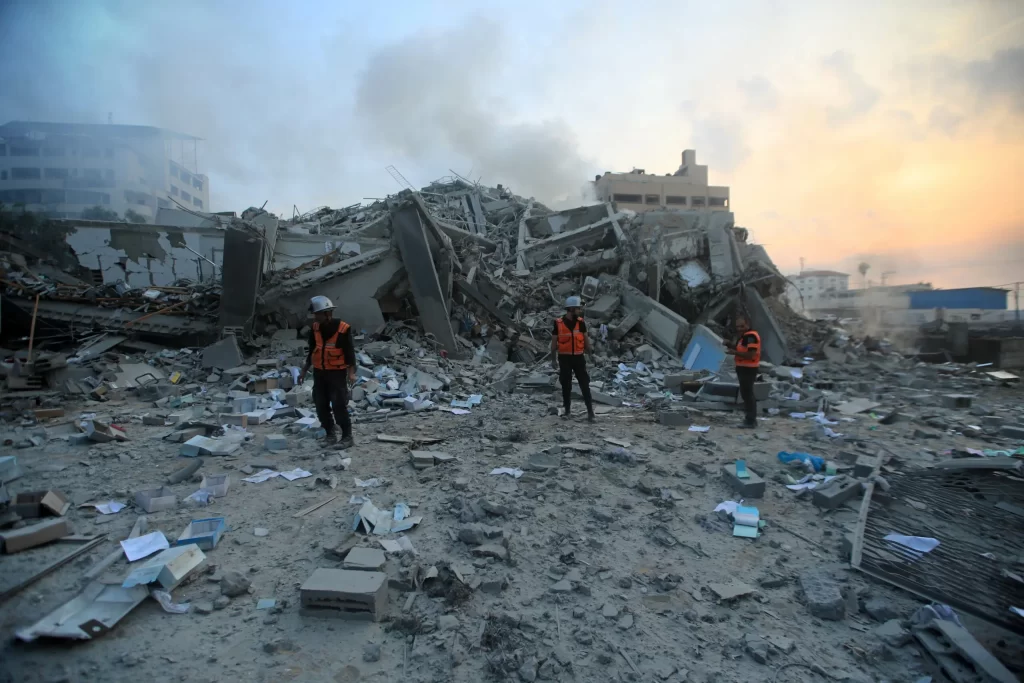

Immediate Economic Impact on Lebanon
The Israel-Lebanon conflict has brought immediate and harsh economic consequences. Due to the conflict, there has been economic paralysis, particularly in southern Lebanon, where many of the clashes are concentrated. Entire villages have been abandoned as civilians flee, causing a sharp decline in tourism revenue, a sector that used to contribute significantly to Lebanon’s GDP. Services have come to a halt, with businesses closing, supply chains disrupted, and transportation infrastructure severely damaged. This paralysis is leading to a grim projection for the country’s economic output in the coming months.

Collapse of Key Sectors: Agriculture, Services, and Industry
Lebanon’s economy heavily relies on sectors such as agriculture, services, and industry, all of which have been significantly affected by the conflict. In agriculture, farmers have been forced to abandon their fields, leading to food shortages and a rise in prices. The services sector, which includes tourism and hospitality, has ground to a halt, with hotels and restaurants closing due to a lack of visitors. Industrial zones in southern Lebanon have also been damaged or shut down, and many factories are unable to operate. This collapse of key sectors further deepens the economic crisis and raises the question of how Lebanon will rebuild these industries after the conflict.
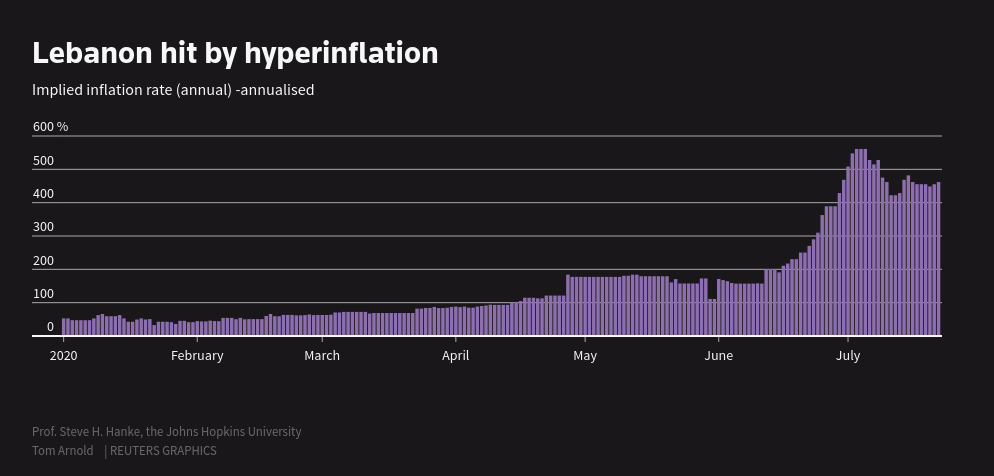
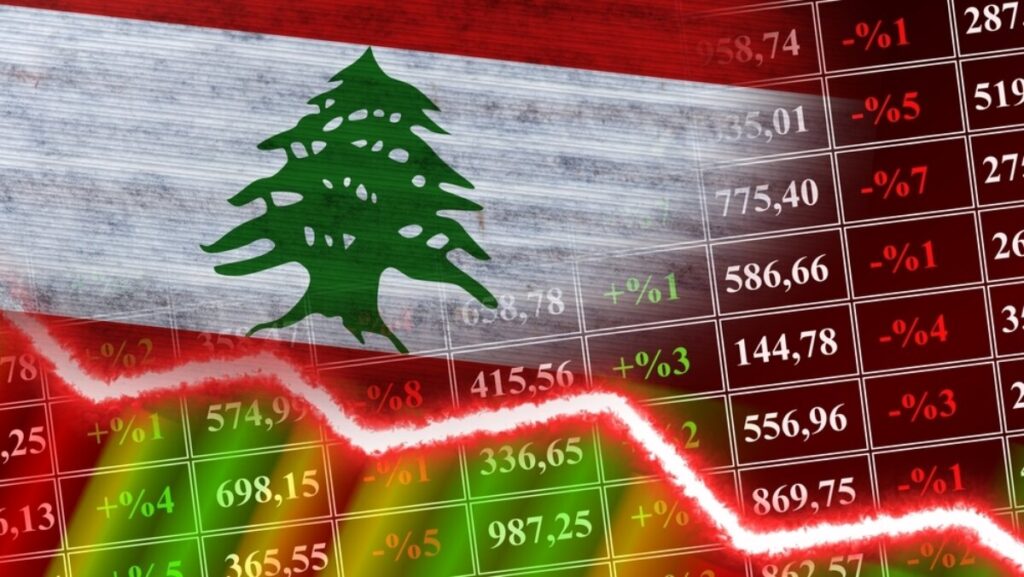
Currency Crisis and Hyperinflation
The Israel-Lebanon conflict has further exacerbated Lebanon’s already dire financial situation. The Lebanese lira, which was already weak due to years of mismanagement, has plummeted in value, resulting in hyperinflation. The price of basic goods such as food and fuel has skyrocketed, and many Lebanese citizens have lost their purchasing power. The central bank is struggling to stabilize the currency, while the government lacks the resources to intervene effectively. With limited foreign reserves and declining investor confidence, Lebanon’s financial future looks bleak, and the war has only sped up its descent into economic chaos.
Financial System and Banking Sector Instability
Before the Israel-Lebanon conflict, Lebanon was already grappling with a banking crisis. With the escalation of the conflict, Lebanon’s financial system has become even more unstable. Bank withdrawals have been limited, and many banks have suspended operations in areas directly affected by the fighting. Trust in the banking sector has hit rock bottom, further crippling the economy. This instability has also worsened Lebanon’s ability to manage its national debt, which has ballooned over the years. With limited access to international financial markets and the absence of foreign aid, Lebanon’s financial crisis shows no signs of easing.

Humanitarian and Social Consequences
The Israel-Lebanon conflict has had significant humanitarian and social consequences, directly tied to the economic consequences of the ongoing war. More than 80% of the Lebanese population is now living below the poverty line, and thousands of people have been displaced. Unemployment rates are soaring as businesses close, and the healthcare system, already under stress, is unable to cope with the growing number of casualties. NGOs are struggling to provide basic services to the displaced population, while the Lebanese government remains overwhelmed and unable to provide adequate assistance. This humanitarian crisis is expected to deepen as the war continues, further aggravating the economic conditions.
Comparison with the 2006 Lebanon-Israel War
The current conflict has drawn comparisons to the 2006 Israel-Lebanon war, but there are key economic differences. In 2006, Lebanon received substantial foreign aid to help rebuild its economy. However, in the current conflict, international financial support has been minimal, leaving Lebanon to fend for itself. Additionally, Lebanon’s financial situation was much stronger in 2006, whereas now, the country is dealing with a near-total economic collapse. This lack of resources and international aid in 2024 has made the economic consequences of the conflict far more severe than in the past.
Loss of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Trade Relationships
The Israel-Lebanon conflict has severely damaged Lebanon’s ability to attract Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). Investors have pulled out of the country due to political instability, and key trade relationships with neighboring countries have been strained. Lebanon’s exports have drastically reduced, as its main trading partners are hesitant to engage in business with a country in conflict. Foreign investors are also withdrawing from real estate projects and infrastructure development, leading to a sharp decrease in much-needed capital flows into the country.
Tourism and Real Estate Collapse
Lebanon has long been a destination for international tourists, contributing significantly to its GDP. However, with the escalation of the Israel-Lebanon conflict, tourism has come to a standstill. There has been a sharp decline in tourism revenue, and hotel occupancy rates have plummeted. The real estate market has also been hit hard, as foreign investors withdraw, and locals are unable to afford property purchases due to the financial crisis. This collapse of tourism and real estate is a significant blow to Lebanon’s economy, further contributing to the economic downturn.
Long-term GDP Contraction and Economic Forecast
The Israel-Lebanon conflict is expected to result in a long-term GDP contraction for Lebanon. The immediate impacts of the war, such as business closures, destruction of infrastructure, and loss of foreign investment, are projected to reduce GDP by more than 20%. Even if the conflict were to end soon, Lebanon’s recovery would be slow and difficult. The government’s fiscal policies are ill-equipped to handle the economic fallout, and without significant reforms and international support, Lebanon faces years of financial hardship.
Agriculture, Ports, and Supply Chain Disruptions
All Business Sectors in Lebanon’s agriculture sector has been one of the hardest hit by the Israel-Lebanon conflict. Many farmers have abandoned their fields, resulting in significant crop losses. Additionally, the country’s ports, particularly those in southern Lebanon, have been severely damaged by airstrikes, disrupting supply chains. Food and fuel shortages have become common, and prices have risen dramatically. The disruption of the agriculture and port sectors further worsens Lebanon’s economic crisis, contributing to rising inflation and poverty.
Regional and Global Economic Repercussions
The Israel-Lebanon conflict has economic consequences that extend beyond the borders of Lebanon. Neighboring countries, including Israel and Syria, have also been affected by disruptions in regional trade routes. Additionally, global oil prices have risen as a result of the instability in the region. The broader global economic repercussions of the conflict include rising energy costs and increased uncertainty in international markets, particularly in the Middle East. These effects are likely to be felt for months, if not years, as the conflict continues to disrupt the region’s economies.
Future Economic Recovery: Challenges and Solutions
Lebanon’s path to economic recovery after the conflict will be fraught with challenges. The country will need substantial international aid to rebuild its infrastructure and economy, but attracting such aid may be difficult given the lack of trust in its financial system. Economic reforms, particularly in the banking sector, will be crucial to restoring investor confidence. Additionally, rebuilding key sectors such as agriculture and tourism will take years, and the government will need to implement policies that support these industries. Without international intervention and a clear recovery plan, Lebanon’s economic future remains uncertain.
Conclusion
The economic consequences of the Israel-Lebanon conflict are devastating and long-lasting. From the collapse of key sectors such as agriculture and tourism to the instability of the financial system and the humanitarian crisis, Lebanon is facing an unprecedented economic catastrophe. With little international aid and a weakened financial system, the road to recovery will be long and difficult for Lebanon. However, with the right reforms and international support, there is hope that the country can rebuild and overcome the challenges posed by this conflict.






One thought on “Economic Consequences of Israel-Lebanon Conflict Intensify”
Comments are closed.